Certified Scrum Master® (CSM) Training

Course Package
Exam Voucher by Scrum Alliance
Official Training Material from Scrum Alliance
Official CSM E-Book
Highly Experienced & Accredited Instructor
Live Instructor-Led Sessions
Real Life Examples & Case Studies
Target Audience of Certified Scrum Master
- Software Engineers
- Product Managers
- Project Managers
- Team Leaders
- Business Analysts
- Development team members
- Testers
- Anyone who would like to build a career as a Scrum Master
Prerequisites

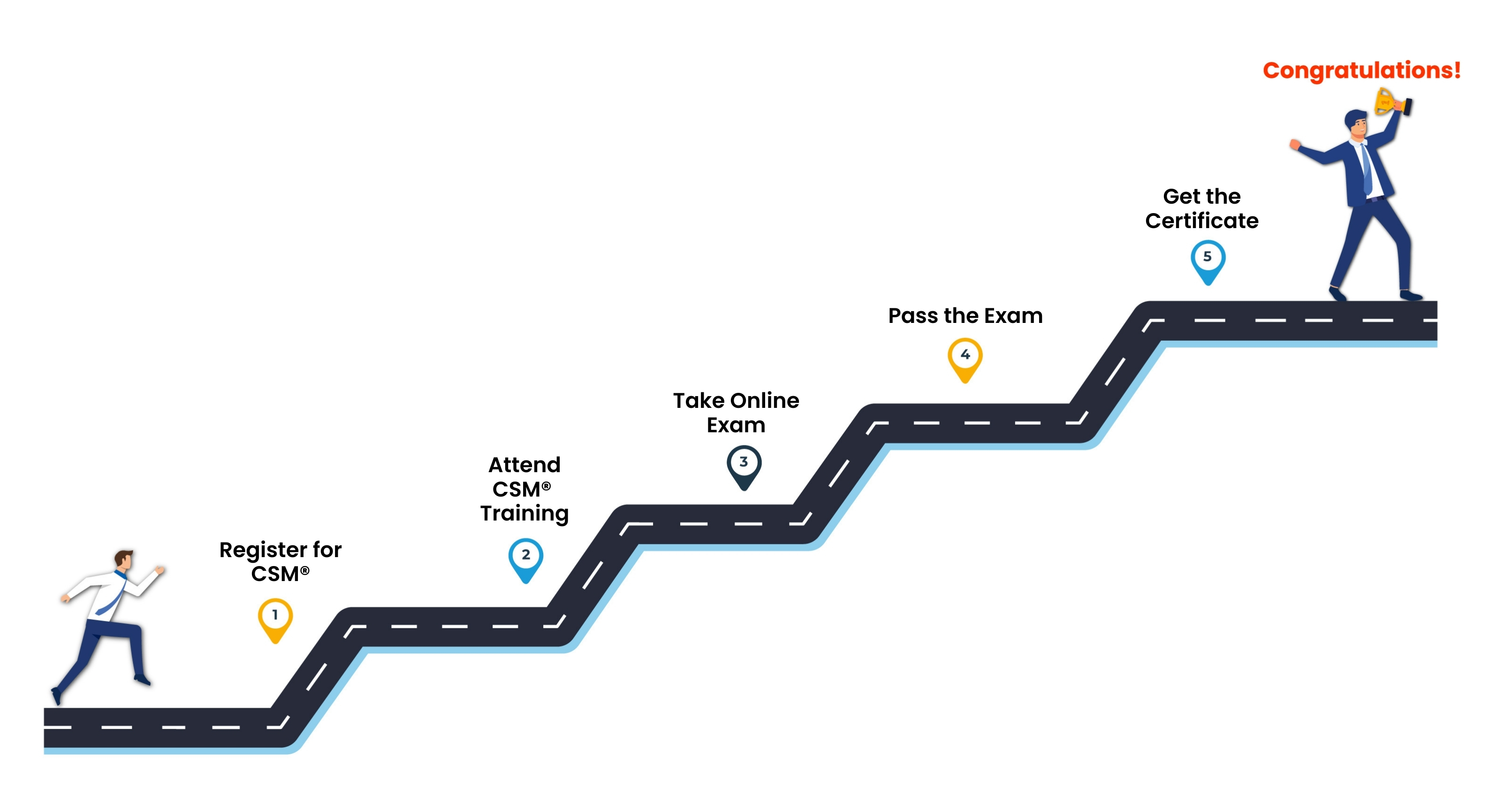
Certified Scrum Master® (CSM) Certification Journey
Course Outline
At the end of this activity, you will be able to-
- Explain the 12 principles and 4 values listed in the Agile Manifesto.
- Demonstrate the benefits of “responding to change” in Agile over “following a plan” in traditional project management.
- Describe how the Scrum values (courage, focus, commitment, respect, openness) relate to the Scrum artifacts, events, and roles.
- List and explain the three pillars in Scrum ― Transparency, Inspection, Adaptation.
- Explain the differences between framework and methodology and understand why Scrum is called a framework.
- List 5 ways to develop an Agile mindset.
- Illustrate 2 differences between Agile and Scrum and explain why these two terms cannot be used interchangeably.
Topics covered
- Agile Manifesto
- 12 Principles
- 4 values
- Scrum Foundations (5 Scrum Values)
At the end of this activity, you will be able to-
- Conduct a retrospective to list 3 techniques to improve the performance and turnaround time.
- Explain the roles and responsibilities of a Scrum Master and a Product Owner.
- List 3 differences between a Scrum Master and a Product Owner and understand why these two roles should not overlap.
- Discuss how a product owner acts as a bridge between the development team and the stakeholders.
- Understand why a Scrum Master is not an active participant but a facilitator in the Scrum events and ceremonies.
- List 3 demerits of having a development team of less than 3 members or greater than 10 members.
Topics covered
- Scrum Master roles and challenges
- Product Owner roles and responsibilities
- Development team roles and responsibilities
Check Our Upcoming Batches
Why Knowlathon







Frequently Asked Questions.
Scrum Master certification FAQs often revolve around the role's responsibilities, course content, and career prospects. Enquirers often seek clarification on Scrum framework principles, Agile methodologies, and facilitation techniques taught in the training. Common queries include prerequisites, such as prior experience or knowledge, and the duration of the certification process, typically spanning a few days to weeks. Certification enhances career opportunities in project management, software development, and Agile environments. FAQs also address exam details, costs, and renewal requirements. Additionally, individuals often seek insights into practical application, mentoring opportunities, and the professional benefits of obtaining Scrum Master certification.
The goal of the Certified Scrum Master (CSM) program is to provide candidates with the information and abilities required to function as a Scrum Master in Agile development teams. The values, roles, events, and artifacts of Scrum are taught to participants along with its concepts. Topics including coaching, servant leadership, facilitation, and dispute resolution are covered throughout the course. Participants receive insights into promoting cooperation, increasing efficiency, and facilitating continuous improvement within Agile teams through interactive discussions and real-world examples. After finishing the course and passing the certification test, participants are acknowledged for their proficiency with Scrum methods as Certified Scrum Masters.











.png)



-foundation.jpg)
-practitioner.jpg)


Student feedback
Reviews